MySQL SQL
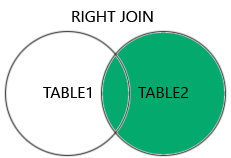
All records from the right table (table 2) and any matching records from the left table (table 1) are returned using the RIGHT JOIN keyword.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
We’ll be using the well-known Northwind sample database in this tutorial.
A sample from the “Orders” table is shown below:
| OrderID | CustomerID | EmployeeID | OrderDate | ShipperID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10308 | 2 | 7 | 1996-09-18 | 3 |
| 10309 | 37 | 3 | 1996-09-19 | 1 |
| 10310 | 77 | 8 | 1996-09-20 | 2 |
And a selection from the “Employees” table:
| EmployeeID | LastName | FirstName | BirthDate | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Davolio | Nancy | 12/8/1968 | EmpID1.pic |
| 2 | Fuller | Andrew | 2/19/1952 | EmpID2.pic |
| 3 | Leverling | Janet | 8/30/1963 | EmpID3.pic |
All employees, along with any orders they may have placed, can be obtained by running the following SQL statement:
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Employees.LastName, Employees.FirstName
FROM Orders
RIGHT JOIN Employees ON Orders.EmployeeID = Employees.EmployeeID
ORDER BY Orders.OrderID;
Note: Even in cases when there are no matches in the left table (Orders), the RIGHT JOIN keyword retrieves all records from the right table (Employees).
CodingAsk.com is designed for learning and practice. Examples may be made simpler to aid understanding. Tutorials, references, and examples are regularly checked for mistakes, but we cannot guarantee complete accuracy. By using CodingAsk.com, you agree to our terms of use, cookie, and privacy policy.
Copyright 2010-2024 by Refsnes Data. All Rights Reserved.