CSS 2D Transforms
CSS 2D Transforms
With CSS transformations, you may skew, scale, rotate, and move elements.
To view a 2D transformation, move your mouse over the element below:
-------ANIMATION MUKAVU-------
You will discover the following CSS attribute in this chapter:
- transform
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the property.

CSS 2D Transforms Methods
With the CSS transform property you can use the following 2D transformation methods:
- translate()
- rotate()
- scaleX()
- scaleY()
- scale()
- skewX()
- skewY()
- skew()
- matrix()
Tip: You will learn about 3D transformations in the next chapter.
The translate() Method

An element is moved using the translate() function from its present location (based on the X- and Y-axis arguments).
The <div> element is moved 50 pixels to the right and 100 pixels down from its existing position in the example that follows:
Example
div {
transform: translate(50px, 100px);
}
The rotate() Method
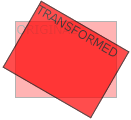
An element can be rotated clockwise or counterclockwise to a specified degree using the rotate() function.
The <div> element is rotated 20 degrees clockwise in the example that follows:
Example
div {
transform: rotate(20deg);
}
Rotating the element counter-clockwise requires the use of negative values.
The <div> element is rotated by 20 degrees counter-clockwise in the following example:
Example
div {
transform: rotate(-20deg);
}
The scale() Method
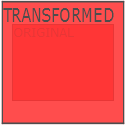
Depending on the values provided for the width and height, the scale() method alters the size of an element.
The <div> element is expanded to three times its original height and twice its original width in the example that follows:
Example
div {
transform: scale(2, 3);
}
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original width and height:
Example
div {
transform: scale(0.5, 0.5);
}
The scaleX() Method
The width of an element can be increased or decreased using the scaleX() method.
In the example that follows, the width of the <div> element is doubled:
Example
div {
transform: scaleX(2);
}
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original width:
Example
div {
transform: scaleX(0.5);
}
The scaleY() Method
The element’s height can be changed using the scaleY() method.
The <div> element is made three times taller in the example that follows:
Example
div {
transform: scaleY(3);
}
The following example decreases the <div> element to be half of its original height:
Example
div {
transform: scaleY(0.5);
}
The skewX() Method
An element can be skewn along the X-axis by the specified angle using the skewX() function.
The <div> element is skewed by 20 degrees along the X-axis in the example that follows:
Example
div {
transform: skewX(20deg);
}
The skewY() Method
An element can be skewn along the Y-axis by the specified angle using the skewY() function.
The <div> element gets skewened by 20 degrees along the Y-axis in the example below:
Example
div {
transform: skewY(20deg);
}
The skew() Method
An element can be skewn along the X and Y axes by the specified angles using the skew() function.
The <div> element is skewened by 20 degrees along the X-axis and 10 degrees along the Y-axis in the example below:
Example
div {
transform: skew(20deg, 10deg);
}
If the second parameter is not specified, it has a zero value. So, the following example skews the <div> element 20 degrees along the X-axis:
Example
div {
transform: skew(20deg);
}
The matrix() Method

All of the 2D transform methods are combined into one by using the matrix() function.
The matrix() function takes six parameters, all of which are mathematical functions that let you skew, rotate, scale, and move (translate) elements.
The matrix(scaleX(), skewY(), skewX(), scaleY(), translateX(), translateY()) contains the parameters.
Example
div {
transform: matrix(1, -0.3, 0, 1, 0, 0);
}
CSS Transform Properties
The following table lists all the 2D transform properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| transform | Applies a 2D or 3D transformation to an element |
| transform-origin | Allows you to change the position on transformed elements |
CSS 2D Transform Methods
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| matrix(n,n,n,n,n,n) | Defines a 2D transformation, using a matrix of six values |
| translate(x,y) | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the X- and the Y-axis |
| translateX(n) | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the X-axis |
| translateY(n) | Defines a 2D translation, moving the element along the Y-axis |
| scale(x,y) | Defines a 2D scale transformation, changing the elements width and height |
| scaleX(n) | Defines a 2D scale transformation, changing the element's width |
| scaleY(n) | Defines a 2D scale transformation, changing the element's height |
| rotate(angle) | Defines a 2D rotation, the angle is specified in the parameter |
| skew(x-angle,y-angle) | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the X- and the Y-axis |
| skewX(angle) | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the X-axis |
| skewY(angle) | Defines a 2D skew transformation along the Y-axis |
