Dart While Loop
When it is unknown how many times a block of code will be executed, the while loop is employed. As long as the condition is met, it will run. It starts by
verifying the provided condition before carrying out the while loop’s statements. Creating an infinite loop is the main application for the while loop.
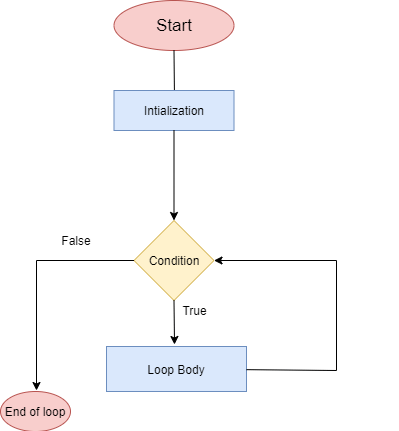
Dart While Loop Flowchart
Syntax
while(condition){
//statement(s);
// Increment (++) or Decrement (--) Operation;
}
In this case, the loop body is executed and the condition is reevaluated if the condition returns true. The loop is ended and control is transferred out of the loop if the condition returns false.
Example
void main()
{
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5)
{
print( i);
++i;
}
}
Output
1
2
3
4
5
Explanation
In the illustration above, we set the integer variable i to 1. The while loop in the following sentence checks if the value of i is higher than or less than 5 for each iteration.
The body of the while loop is executed and the condition is rechecked if the condition returns true. Until the condition is no longer true, it will continue.
The loop is then ended when the value of i is 6, which violated the requirement. On the console, the numbers 1 through 5 were shown.
Infinite While Loop
An infinite while loop occurs when the while loop runs indefinitely. Let’s examine the example of the infinite loop.
Example
void main()
{
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5)
{
print( i);
--i;
}
}
The code above has only had one change made to it. Every time the while loop iterated, we decreased the value of i. As a result, it will never satisfy the given condition and turn into an endless loop.
Example
void main()
{
while (true)
{
print("Welcome to JavaTpoint");
}
}
The provided statement will be printed endlessly. An endless loop is created automatically when we declare a Boolean expression to be true in a while loop.
Logical Operator while loop
Occasionally, we must verify the various criteria within a while loop. By employing logical operators like (||, &&, and!), we may accomplish this. Let’s examine the subsequent ideas.
- while (n1<5 && n2>10) – If both of these are met, it will run.
- while (n1<5 || n2>10) – If any of the conditions are met, it will run.
- while(!n1 = 10) – If n1 is less than or equal to 10, it will run.
Example
void main() {
int n1=1;
int n2=1;
// We are checking multiple condition by using logical operators.
while (n1 <= 4 && n2 <= 3)
{
print("n1 : ${n1}, n2: ${n2}");
n1++;
n2++;
}
}
Output
n1 : 1, n2: 1
n1 : 2, n2: 2
n1 : 3, n2: 3
Explanation
Two variables, n1 and n2, have the value 1 given to them in the code above. We now examined several cases in the while loop when n1 and n2 are less than or equal to 4 and 3, respectively.
It tested both values and printed the outcome on the first iteration. There comes a time when n1 and n2 add up to 4. The loop was stopped and the result was displayed on the screen because while n1 met condition one, n2 did not meet condition two.
