Dart Typedef
To produce an alias for a function type in Dart, use typedef. This alias may then be used as a type annotation to declare variables and return types of the function type. When defining a variable or function return type, an alias of the function type can be used as a type annotation. When we assign the function type to a variable, the type information is stored in a typedef.
Declaring a typedef
To construct an alias for a function that will be identical to the original functions, use the typedef keyword. A function prototype with a set of parameters can also be made. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
typedef function_name(parameters)
Example
Let’s construct an alias for MultiOperation(int n1, int n2) that takes two integer-type parameters.
typedef MultiOperation(int n1, int n2); // function signature
Assigning typedef Variable
The typedef variable can be assigned to any function that has the same parameter. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
type_def var_name = function_name;
Now let’s examine the following example, in which two functions are defined that share the same signature as the MultiOperation.
Sum(int n1, int n2) {
print("Sum of the two number:${n1+n2}");
}
Sub(int n1, intn2 ) {
print("Subtraction of the two number:${n1-n2}");
}
Calling Function with typedef
With the typdef variable, we may use the same parameter to invoke the function. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
var_name(parameter);
Example
MultiOperation mp;
mp = Sum;
mp(20,10);
mp = Sub;
mp(30,20);
Any method that takes two integer parameters can be referenced using the typedef variable mp. Using typedefs, one can change the function reference at runtime.
Complete Program using typedef
Example
typedef MultiOperation(int num1, int num2); // typedef function signature
Sum(int n1, int n2) {
print("Sum of the two number:${n1+n2}");
}
Sub(int n1, int n2 ) {
print("Subtraction of the two number:${n1-n2}");
}
void main() {
MultiOperation mp = Sum;
print("JavaTpoint - Dart typedef Example");
mp(20,10);
mp = Sub;
mp(30,20);
}
Output
JavaTpoint - Dart typedef Example
Sum of the two numbers: 30
Subtraction of the two numbers: 10
Explanation
The typedef keyword was used in the code above to establish the MultiOperation() function’s alias. The functions Sum() and Sub() that we have constructed share the same signature as the typedef function.
Next, we allocated the typedef variable mp, which pointed to the functions Sub() and Sum(). The function was now called by feeding it the necessary argument, and the output was displayed on the screen.
Typedef as Parameter
The typedef approach is available to us as an option. The program NumericOperaion(int n1, int n2, MultiOperation mp) above has two integer variables. In the example below, we are creating an additional function to it with typedef ManyOperation mp as its parameter and the two integer variables.
Example
typedef MultiOperation(int num1, int num2); // typedef function signature
Sum(int n1, int n2) {
print("Sum of the two number:${n1+n2}");
}
Sub(int n1, int n2 ) {
print("Subtraction of the two number:${n1-n2}");
}
NumericOperation(int n1, int n2, MultiOperation mp){
print("Inside Operation");
mp(n1,n2);
}
void main() {
print("JavaTpoint - Dart typedef Example");
NumericOperation(20, 10, Sum);
NumericOperation(20, 10, Sub);
}
Output
JavaTpoint - Dart typedef Example
Inside Operation
Sum of the two number: 30
Inside Operation
Subtraction of the two number: 10
In the above code, we didn’t need to create a typedef variable to the refer to each method; we just called the NumericOperation() function by passing the required value and typedef variable mp. It performed the given operations and printed the result.
Dart Debugging
The process of finding and removing errors—both current and potential—from the Dart program that could lead to confusion and doubt when the program is being executed is known as debugging. Debugging is necessary to find and address issues so that the program can function without hiccups or smoothly.
Using the Dart program’s integrated development environment (IDE) facilitates debugging. We’re going to assume that you have WebStorme installed on your PC, which is the most popular and appropriate IDE. Using the WebStorm Editor, we may troubleshoot something step-by-step.
What are Breakpoints?
Breakpoints are program checkpoints that are used to halt the program at a certain point in order to examine its behavior. To check for flaws in that particular portion of the software, we can add breakpoints.
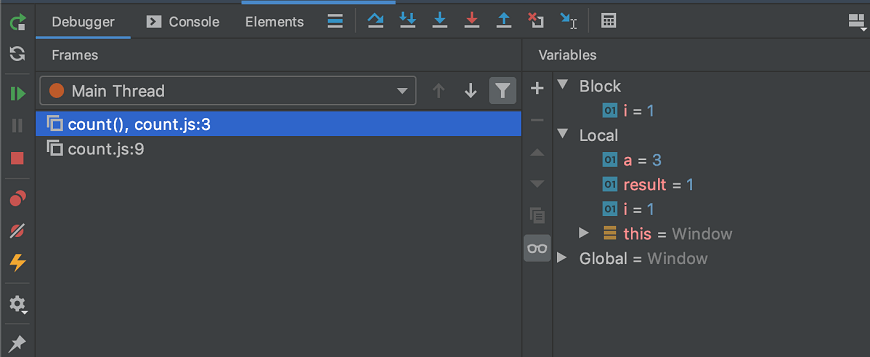
How to add Breakpoints in WebStorm?
In WebStorm, adding a breakpoint is as easy as clicking on a line number in the left bar. Run the program in debug mode after adding the breakpoints, and it will display the Debugger window where we can confirm that the breakpoint is functioning as intended. In the watches pane, we can also alter the values and observe the changes.