Dart Lists
An array, which is an ordered collection of things, is comparable to a dart list. Any other programming language’s most widely used and well-liked collection is called an array. The JavaScript array literals appear similar to the Dart list. The list declaration syntax is provided below.
var list1 = [10, 15, 20,25,25]
All elements are stored inside the square bracket ([]) and separated by commas (,) to define the Dart list.
Let’s understand the graphical representation of the list –
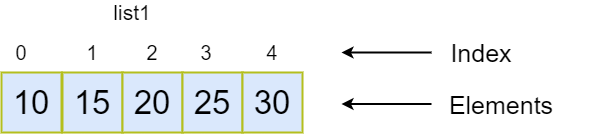
list1: The list object is referred to by the list variable.
Index: Every element in the list has an index number that indicates its location. To retrieve a specific element from the list, such as list_name[index], utilize its index number. List indexing begins at 0 and goes all the way up to length-1, where length is the number of each member in the list. For instance, the list above has four entries.
Elements: The actual value or dart object that is kept in the specified list is referred to as the list elements.
Types of Lists
Two sorts of Dart lists can be distinguished:
- Fixed Length List
- Growable List
Fixed Length List
The supplied length is used to define the fixed-length lists. The size cannot be altered at runtime. Below is the syntax.
Syntax – Create the list of fixed-size
var list_name = new List(size)
The list of fixed size is created using the syntax shown above. At runtime, we are unable to add or remove an element. If someone attempts to change its size, an exception will be raised.
The following is the syntax for initializing the fixed-size list element.
Syntax – Initialize the fixed size list element
list_name[index] = value;
Example
void main() {
var list1 = new List(5);
list1[0] = 10;
list1[1] = 11;
list1[2] = 12;
list1[3] = 13;
list1[4] = 14;
print(list1);
}
Output
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
Explaination
The list of fixed size is referenced by the variable list1, which we defined in the example above. The list has five entries, and we added the elements based on each index position, so the 0th index has 10, the 1st index contains 12, and so on.
Growable List
A list that is stated without a size restriction is called a growable list. Runtime changes can be made to the Growable list’s size. The following is the syntax for declaring a Growable list.
Syntax - Declaring a List
// creates a list with values
var list_name = [val1, val2, val3]
Or
// creates a list of the size zero
var list_name = new List()
Syntax - Initializing a List
list_name[index] = value;
Example
void main() {
var list1 = [10,11,12,13,14,15];
print(list1);
}
Output
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
The empty list or List() constructor is what we’re using to create a list in the example below. To add an element dynamically to the provided list, use the add() method.
Example
void main() {
var list1 = new List();
list1.add(10);
list1.add(11);
list1.add(12);
list1.add(13);
print(list1);
}
Output
[10, 11, 12, 13]
List Properties
The list’s attributes are shown below.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| first | It returns the first element case. |
| isEmpty | It returns true if the list is empty. |
| isNotEmpty | It returns true if the list has at least one element. |
| length | It returns the length of the list. |
| last | It returns the last element of the list. |
| reversed | It returns a list in reverse order. |
| Single | It checks if the list has only one element and returns it. |
Inserting Element into List
There are four techniques available in Dart that are used to add elements to lists. These techniques are listed below.
- add()
- addAll()
- insert()
- insertAll()
The add() Method
The supplied value is inserted at the end of the list using this method. It returns the updated list object and has the ability to add elements one at a time. Let’s examine the subsequent illustration:
Syntax
list_name.add(element);
Example
void main() {
var odd_list = [1,3,5,7,9];
print(odd_list);
odd_list.add(11);
print(odd_list);
}
Output
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]
Explanation
In The list called odd_list in the example above contains odd numbers. We used the add() function to introduce a new element, number 11. The changed list was returned by the add() method, which added the element at the end of the list.
The addAll() Method
Multiple values can be inserted into the provided list using this function. Square brackets ([]) encompass each value and are used to separate them. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.addAll([val1,val2,val3,?..valN]);
Example
void main() {
var odd_list = [1,3,5,7,9]
print(odd_list);
odd_list.addAll([11,13,14]);
print(odd_list);
}
Output
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 14]
Explanation
In the above example, we don’t need to call the add() function multiple times. The addAll() appended the multiple values at once and returned the modified list object.
The insert() Method
The insert() method provides the facility to insert an element at specified index position. We can specify the index position for the value to be inserted in the list. The syntax is given below.
Syntax
list_name.insert(index,value);
Example
void main(){
List lst = [3,4,2,5];
print(lst);
lst.insert(2,10);
print(lst);
}
Output
[3, 4, 2, 5]
[3, 4, 10, 2, 5]
Explanation
We don’t need to use the add() function more than once in the example above. The changed list object was returned by the addAll() function, which simultaneously added numerous values.
The insertAll() Method
An element can be inserted at a particular index position using the insert() method. For the value to be added to the list, we can designate the index position. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.insertAll(index, iterable_list_of_value)
Example
void main(){
List lst = [3,4,2,5];
print(lst);
lst.insertAll(0,[6,7,10,9]);
print(lst);
}
Output
[3, 4, 2, 5]
[6, 7, 10, 9, 3, 4, 2, 5]
Explanation
Using the insertAll() function, we have inserted the list of values at the 0th index point in the example above. The changed list object was returned.
Updating List
The list can be updated with the help of the Dart; all we need to do is access the element and change its value. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name[index] = new_value;
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [10,15,20,25,30];
print("List before updation: ${list1}");
list1[3] = 55;
print("List after updation:${list1}");
}
Output
List before updation: [10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
List after updation: [10, 15, 20, 55, 30]
Explanation
In the example above, we accessed the third index, changed the value to 55, and then printed the outcome. The new value of 55 was added to the previous list.
replaceRange(): This replaceRange() function, available in Dart, is used to update within a specified range of list items. It modifies the elements’ values inside the given range. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.replaceRange(int start_val, int end_val, iterable);
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [10,15,20,25,30];
print("List before updation: ${list1}");
list1.replaceRange(0,4,[1,2,3,4]) ;
print("List after updation using replaceAll() function : ${list1}");
}
Output
List before updation: [10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
List after updation using replaceAll() function : [1, 2, 3, 4, 30]
Explanation
The replaceRange() function was called to the list that takes the three inputs in the example above. As third inputs, we gave the list of components to be replaced, the end index, and the starting index, which is the zeroth. The updated list containing the substituted entry from the specified range was returned.
Removing List Elements
The functions listed below are offered by Dart to eliminate list elements.
- remove()
- removeAt()
- removeLast()
- removeRange()
The remove() Method
It eliminates each item from the provided list one at a time. Element is accepted as an argument. If there are several instances of the same element in the list, it eliminates the first instance. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.remove(value)
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [10,15,20,25,30];
print("List before remove element : ${list1}");
list1.remove(20) ;
print("List after removing element : ${list1}");
}
Output
List before remove element : [10, 15, 20, 25, 30]
List after removing element : [10, 15, 25, 30]
Explanation
The remove() function was called to the list in the example above, and the value 20 was supplied as an input. The 20 was taken out of the provided list, and the updated list was given back.
The removeAt() Method
An element is taken out of the designated index position and returned. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.removeAt(int index)
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [10,11,12,13,14];
print("List before remove element : ${list1}");
list1.removeAt(3) ;
print("List after removing element : ${list1}");
}
Output
List before remove element : [10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
List after removing element : [10, 11, 12, 14]
Explanation
In the example above, the element 13 was deleted from the list by using the third index position as an argument to the removeAt() function.
The removeLast() Method
The last element in the supplied list is eliminated using the removeLast() function. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name.removeLast()
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [12,34,65,76,80];
print("List before removing element:${list1}");
list1.removeLast();
print("List after removed element:${list1}");
}
Output
List before removing element:[12, 34, 65, 76, 80]
List after removed element:[12, 34, 65, 76]
Explanation
The removeLast() method was used in the example above, and it deleted and returned the final element (80) from the supplied list.
The removeRange() Method
The object inside the designated range is removed using this procedure. The two inputs that it takes are the start index and finish index. All elements that fall within the designated range are eliminated. Below is the syntax.
Syntax
list_name. removeRange();
Example
void main(){
var list1 = [12,34,65,76,80];
print("List before removing element:${list1}");
list1.removeRange(1,3);
print("List after removed element:${list1}");
}
Output
List before removing element:[12, 34, 65, 76, 80]
List after removed element:[12, 76, 80]
Explanation
In the example above, start index position 1 and finish index position 3 were supplied as arguments when the removeRange() method was called. Everything that belonged between the designated position was eliminated.
Dart Iterating List elements
The forEach method can be used to cycle through the Dart List. Let’s examine the subsequent illustration.
Example
void main(){
var list1 = ["Smith","Peter","Handscomb","Devansh","Cruise"];
print("Iterating the List Element");
list1.forEach((item){
print("${list1.indexOf(item)}: $item");
});
}
Output
Iterating the List Element
0: Smith
1: Peter
2: Handscomb
3: Devansh
4: Cruise
