Dart Inheritance
The process of obtaining the traits and attributes of another class is known as dart inheritance. It offers the capability of generating a new class from an already-existing one. It is the oops’ (Object-Oriented Programming Approach) most fundamental idea. All of the traits and behaviors from the prior class can be carried over to the current one.
- Parent Class: A class is referred to as a parent class or super class if it is inherited by another class. It goes by the name “base class” as well.
- Child Class: A class is referred to as a child class if it inherits properties from another class. It is sometimes referred to as the subclass or derived class.
Assume we have a fleet of automobiles and designate Duster, Maruti, and Jaguar as the three classes. For each of the three classes, the identical methods—modelName(), milage(), and man_year()—will be used. We can avoid writing these functions in each of the three classes by utilizing inheritance.

The accompanying graphic illustrates what would happen if we created a class called Car and wrote the common function in each class. Consequently, the program’s duplication and data redundancy will increase. This kind of issue is avoided by using inheritance.
By include these functions in the Car class definition and inheriting from it in the other classes, we can prevent data redundancy. It improves the code’s capacity for reuse. Rather than writing the function several times, we only need to write it once. Let’s examine the subsequent picture.

Syntax
class child_class extends parent_class {
//body of child class
}
By employing the extends keyword, the child class inherits the parent class’s variables, functions, and properties. We shall talk about this idea later. It cannot inherit the parent class constructor.
Types of Inheritance
There are primarily four types of inheritance. They are listed below.
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
Single Level Inheritance
A class is inherited by one parent class and one subclass is inherited by one parent class in a single inheritance. We build a Person object in the example below, which is derived from the Human class.

Example
class Bird{
void fly()
{
print("The bird can fly");
}
}
// Inherits the super class
class Parrot extends Bird{
//child class function
void speak(){
print("The parrot can speak");
}
}
void main() {
// Creating object of the child class
Parrot p=new Parrot();
p.speak();
p.fly();
}
Output
The parrot can speak
The bird can fly
Explanation
The fly() function is declared in the parent class Bird that we created in the code above. Next, we used the extends keyword to create the child class Parrot, which inherited the properties of its parent class. The function speak() is unique to the child class.
Fly() and talk() are the two new functions in the child class. As a result, we generated a child class object and used both functions. The outcome was printed onto the console.
Multilevel Inheritance
A subclass either starts the chaining of inheritance or is inherited by another subclass in multiple inheritance. Let’s examine the next illustration.
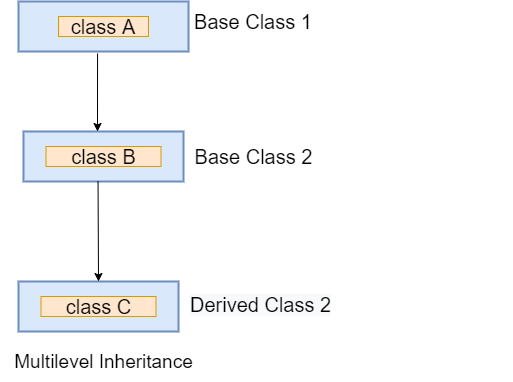
Example
class Bird{
void fly()
{
print("The bird can fly");
}
}
// Inherits the super class
class Parrot extends Bird{
void speak(){
print("The parrot can speak");
}
}
// Inherits the Parror base class
class Eagle extends Parrot {
void vision(){
print("The eagle has a sharp vision");
}
}
void main() {
// Creating object of the child class
Eagle e=new Eagle();
e.speak();
e.fly();
e.vision();
}
Output
The parrot can speak
The bird can fly
The eagle has a sharp vision
Explanation
The Eagle class was formed in the example above, and it was inherited from the Parrot class. Eagle’s parent class is now the parrot, and Eagle has inherited all of the functions from both parent classes. We generated the child class object and had access to all of its properties. The output was displayed on the screen.
Hierarchical Inheritance
A single class is inherited by two or more classes in a hierarchical inheritance. The Person class is inherited by Peter and James, the two child classes in the example below.

Example
// Parent Class
class Person {
void dispName(String name) {
print(name);
}
void dispAge(int age) {
print(age);
}
}
class Peter extends Person {
void dispBranch(String nationality) {
print(nationality);
}
}
//Derived class created from another derived class.
class James extends Person {
void result(String result){
print(result);
}
}
void main() {
// Creating Object of James class
James j = new James();
j.dispName("James");
j.dispAge(24);
j.result("Passed");
// Creating Object of Peter class
Peter p = new Peter();
p.dispName("Peter");
p.dispAge(21);
p.dispBranch("Computer Science");
}
Output
James
24
Passed
Peter
21
Computer Science
