iOS: Progress View
The ProgressView is a tool used in iOS applications to show a task’s progress over time. The UIProgressView instance, which is derived from the UIView class, is known as the ProgressView.
class UIProgressView : UIView
The Progress View shows the progress bar, and we can adjust its style using the UI Progress View class’s attributes and methods. We are able to obtain and modify the values linked to a task’s progress.
Properties and methods
| SN | Property or method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | var progress: Float | It represents the current progress shown by the progress bar. |
| 2 | func setProgress(Float, animated: Bool) | This method is used to set the progress of the progress bar. We can optionally pass a Boolean value to determine whether the animation would be on or off. |
| 3 | var observedProgress: Progress? | It is the progress object which is used to update the progress view. |
| 4 | var progressViewStyle: UIProgressView.Style | It represents the current graphical style of the progress view. |
| 5 | var progressTintColor: UIColor? | It is the color that is displayed for the portion of the progress bar that is filled or completed. |
| 6 | var progressImage: UIImage? | By using this property, we can set the image for the portion of the progress bar that is filled. |
| 7 | var trackTintColor: UIColor? | It is the color that is displayed for the portion of the progress bar; this is not filled or not completed. |
| 8 | var trackImage: UIImage? | It is the image that can be displayed for the portion of the progress bar that is not filled. |
Adding Progress View to the Interface Builder.
Find the UI Progress View in the object library and drag the result to the storyboard to add the Progress View, as seen in the following illustration.

Establish the progress view’s auto-layout rules to control its size and location on various screen sizes.
To control how the progress view changes over time, adjust the relevant UIProgressView settings.
Example
We will mimic the sign-up process in this example, asking the user to fill out their name, email address, and password in order to register for the application. We will display a progress bar to the user when tapping the submit button, letting them know that their data is being saved in the database.
Interface Builder
In order to construct the project’s interface, we will add a submit button, four text fields, and a sign-up label to the storyboard. We will also establish the auto-layout rules that will control the fields’ sizes and positions, as seen in the image below.

As seen in the accompanying image, let’s now add the progress view and a label to the interface to show the progress.

We will start a timer to show the progress of the progress view when the user presses the submit button.
ViewController.swift
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var nameTF: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var emailTF: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var passwordTF: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var CFPasswordTF: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var progressView: UIProgressView!
@IBOutlet weak var msgLbl: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var sbmtBtn: UIButton!
let progress = Progress(totalUnitCount: 4)
var ratio: Float?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
progressView.isHidden = true
ratio = 0
progressView.progress = ratio!
msgLbl.isHidden = true
progressView.layer.cornerRadius = 10
sbmtBtn.layer.cornerRadius = 10
}
@IBAction func clickedSubmitBtn(_ sender: Any) {
if(nameTF.text != "" && emailTF.text != "" && passwordTF.text != ""){
sbmtBtn.isHidden = true
msgLbl.isHidden = false
progressView.isHidden = false
Timer.scheduledTimer(withTimeInterval: 1.0, repeats: true) { (timer) in
guard self.progress.isFinished == false else{
timer.invalidate()
self.msgLbl.text = "Data Saved"
return
}
self.progress.completedUnitCount += 1
let progrsssFloat = Float(self.progress.fractionCompleted)
self.progressView.setProgress(progrsssFloat, animated: true)
}
}
}
}
Output

Supplementary Views
The supplemental views can also be used by a CollectionView to display the data. The section headers and footers that are set up using the UICollectionViewDelegate methods are the supplemental views. The layout object for the collection view can define support for additional views. The locations of those views are likewise specified by the collection view layout object.
CollectionView Delegate methods
The UICollectionViewDatasource protocol is adopted by the CollectionView Datasource. The data requested by the collectionview must be provided by the collection view datasource object. It resembles the data model of the collectionview application. The data is passed to the collectionview for display.
The methods declared in the UICollectionViewDataSource protocol are shown in the following table.
| SN | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, shouldSelectItemAt: IndexPath) -> Bool | This method asks the delegate to select the item at an indexpath. |
| 2 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, didSelectItemAt: IndexPath) | This method tells the delegate to select the item at an indexpath. This method is executed when the item at an indexpath in then collectionview is selected. |
| 3 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, shouldDeselectItemAt: IndexPath) -> Bool | This method asks the delegate to deselect the item at an indexpath. |
| 4 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, didDeselectItemAt: IndexPath) | This method is executed when the item at an indexpath in the collectionview is deselected. |
| 5 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, shouldBeginMultipleSelectionInteractionAt: IndexPath) -> Bool | It asks the delegate whether the multiple items can be selected using the two-finger pan gesture in the collection view. |
| 6 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, didBeginMultipleSelectionInteractionAt: IndexPath) | This method is executed when the multiple items are selected using the two-finger pan gesture. |
| 7 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, shouldHighlightItemAt: IndexPath) -> Bool | It asks then delegate whether to highlight the item during tracking. |
| 8 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, didHighlightItemAt: IndexPath) | This method is executed when the item is highlighted in the collectionview at some indexpath. |
CollectionView DataSource Methods
The UICollectionViewDatasource protocol is adopted by the CollectionView Datasource. The data requested by the collectionview must be provided by the collection view datasource object. It resembles the data model of the collectionview application. The data is passed to the collectionview for display.
The methods declared in the UICollectionViewDataSource protocol are shown in the following table.
| SN | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection: Int) -> Int | This method returns an integer representing the number of items in section to be displayed in the collectionview. It is the count of the array of data associated with the collectionview. |
| 2 | func numberOfSections(in: UICollectionView) -> Int | This method returns an integer representing the number of sections to be displayed in the collectionview. |
| 3 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, cellForItemAt: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell | This method returns the instance of UICollectionViewCell which is configured to display the actual content. This method is not optional and to be defined if the view controller is conforming UICollectionViewDataSource protocol. |
| 4 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, viewForSupplementaryElementOfKind: String, at: IndexPath) -> UICollectionReusableView | This method asks the data source object to provide a supplementary view to display in the collection view. |
| 5 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, canMoveItemAt: IndexPath) -> Bool | It asks the datasource object whether the specified item can be moved to another location in the collectionview. |
| 6 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, moveItemAt: IndexPath, to: IndexPath) | This method moves the specified item to the specified indexpath. |
| 7 | func indexTitles(for: UICollectionView) -> [String]? | This method returns the array of the string containing the titles of the indices. |
| 8 | func collectionView(UICollectionView, indexPathForIndexTitle: String, at: Int) -> IndexPath | It asks the data source object to return the index path of a collection view item that corresponds to one of the index entries. |
Example 1
In this example, a collection view will be used to display a grid of things on the screen.
Interface Builder (main.storyboard)
Find the collectionview in the object library and drag the result into the interface builder to add it to the project’s storyboard. The collectionview will now be a part of the UI. Set the collection view’s auto-layout rules now to control its size and placement across various screen sizes. The collectionview cell displays the CollectionView’s real content. In the Xcode attribute inspector, we must declare the properties for the cell. In this example, we set the text for the label in the data source method on the cell object and add the label to the collectionview cell.
The following image displays the properties assigned to the collectionview cell.
The following graphic displays the attributes assigned to the collection view.
The project’s interface builder can be seen below.
ViewController.swift
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
var itemArr = Array<String>()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
collectionView.delegate = self
collectionView.dataSource = self
for i in 1...60{
itemArr.append(i.description)
}
}
}
extension ViewController : UICollectionViewDelegate{
}
extension ViewController : UICollectionViewDataSource{
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return itemArr.count
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: "cell", for: indexPath) as! MyCollectionViewCell
cell.myLbl.text = itemArr[indexPath.item]
cell.myLbl.layer.borderColor = UIColor.blue.cgColor
cell.myLbl.textAlignment = .center
cell.myLbl.layer.cornerRadius = 10
cell.myLbl.layer.borderWidth = 2
return cell
}
}
MyCollectionViewCell.swift
import UIKit
class MyCollectionViewCell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var myLbl: UILabel!
}
Output
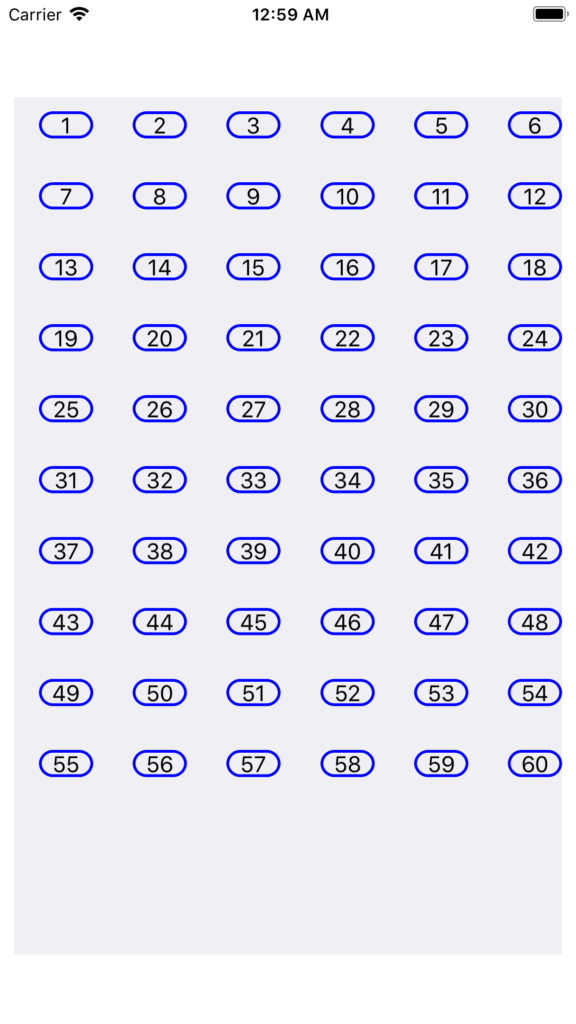
CollectionView Demo Project
This example demonstrates the intended use of the collection view in iOS applications. This application displays several products on a view controller scene, simulating an e-commerce application. When we click on a product, a new screen with a thorough view of that particular product appears.
Two view controllers will be used in this application, and they will be embedded within the navigation controller to enable navigating via the view controllers. It is recommended that you possess a rudimentary understanding of navigation controllers, which is what this lesson covers.
Interface Builder (main.storyboard)
In this project, a collectionview will be used to display a scene in the application that resembles a grid. Drag the resultant collection view to the storyboard after doing a search for it in the object library.
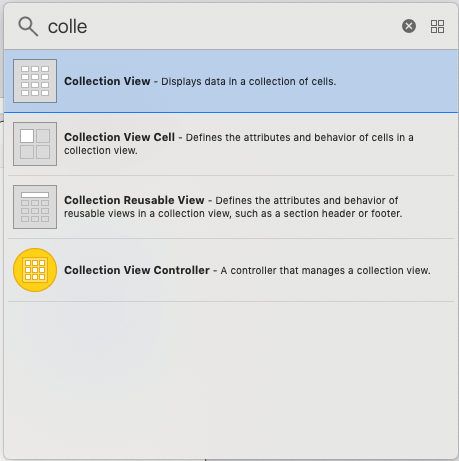
Configure the cell
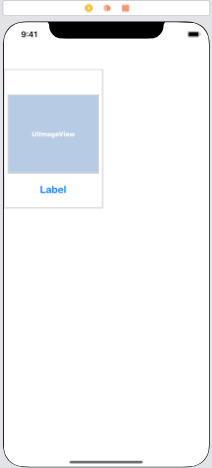
The prototype cell that will display the real item on the screen needs to be configured now. The picture view and label for the product image and image name, respectively, will be located in the prototype cell. To establish the connection outlets for the imageview and label, respectively, add the imageview and the label to the collectionview cell and give the cell the class DemoCollectionViewCell.swift.
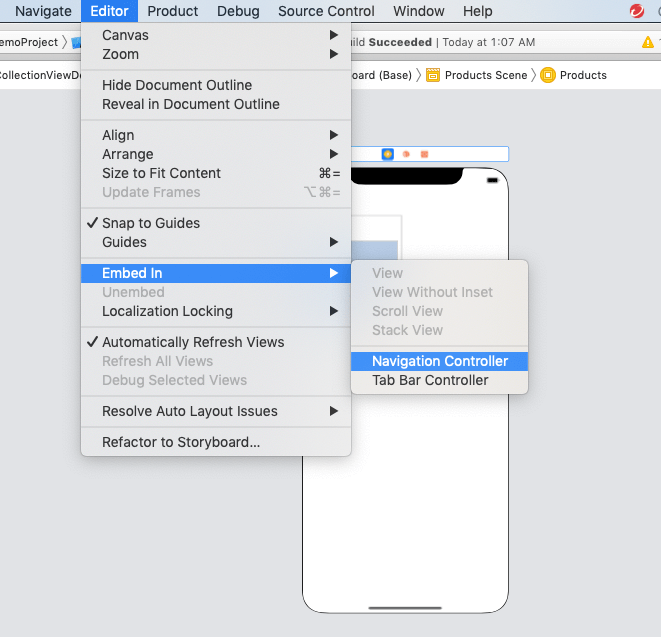
Add the navigation controller
The view controller will be selected, the editor will be clicked, and the option to embed in will be selected, as seen in the following image, to embed the view controller to a navigation controller.
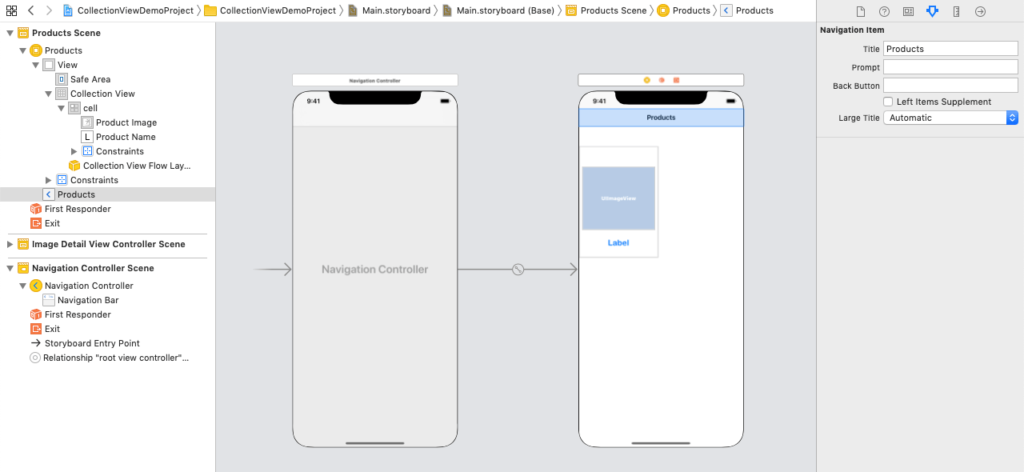
A navigation bar appears on all view controllers by default when we embed our view controllers into the navigation controller. We are able to change the navigation bar’s title. When we talk about navigation interface later in this lesson, we will have studied more about navigation controllers. The view controller and navigation controller, for which we have set the navigation bar title to Products, are displayed in the following image.
Adding ImageDetailViewController
We require a ViewController to display product details to the interface builder. We will add ViewController to the interface builder and give this ViewController the class ImageDetailViewController in order to accomplish this.
We will add the ImageView and the label to the ViewController to the imageDetailViewController. Additionally, we’ll set the navigation bar title to “Product Details” and integrate this view controller into our navigation controller.
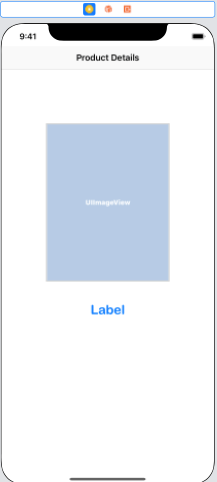
When an item in the CollectionView is selected, the ImageDetailViewController will be shown. To access this view controller, we will put the following code in the collectionview datasource method.
let imageDetailVC = self.storyboard?.instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: "ImageDetailViewController") as! ImageDetailViewController
imageDetailVC.img = imgArr[indexPath.row]
imageDetailVC.name = lblArr[indexPath.row]
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(imageDetailVC, animated: true)
The back button on a view controller that receives a push from a navigation controller activates, allowing the view controller to move backward in the storyboard.
The following image displays the interface builder that was included in the sample project.
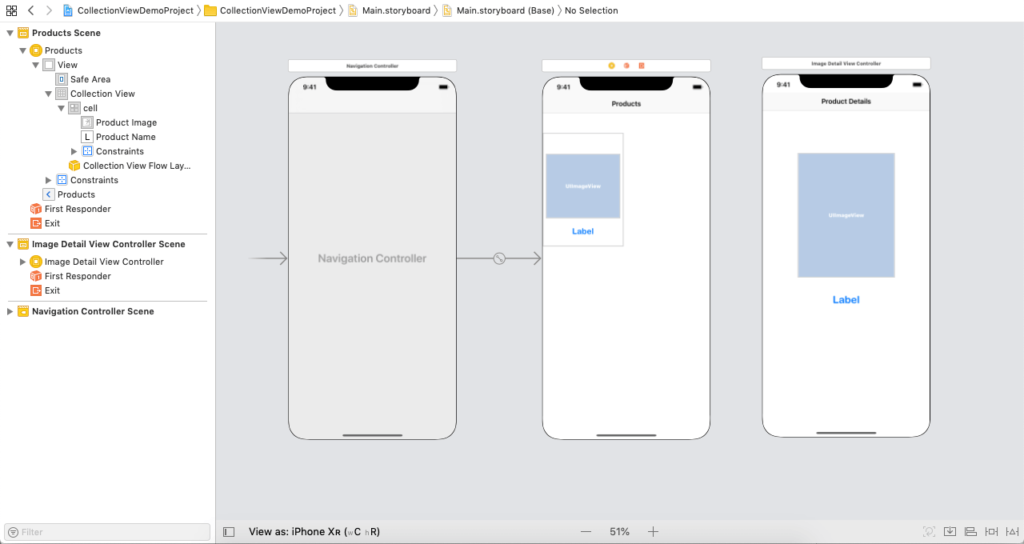
ViewController.swift
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
var imgArr = Array<UIImage>()
var lblArr = Array<String>()
@IBOutlet weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
collectionView.delegate = self
collectionView.dataSource = self
for i in 1...10{
lblArr.append("Watch"+i.description)
}
imgArr = [ imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1"), imageLiteral(resourceName: "watch1")]
}
}
extension ViewController:UICollectionViewDataSource{
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return lblArr.count
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: "cell", for: indexPath) as! DemoCollectionViewCell
cell.productImage.image = imgArr[indexPath.row]
cell.productName.text = lblArr[indexPath.row]
return cell
}
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, didSelectItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
let imageDetailVC = self.storyboard?.instantiateViewController(withIdentifier: "ImageDetailViewController") as! ImageDetailViewController
imageDetailVC.img = imgArr[indexPath.row]
imageDetailVC.name = lblArr[indexPath.row]
self.navigationController?.pushViewController(imageDetailVC, animated: true)
}
}
extension ViewController:UICollectionViewDelegate{
}
ImageDetailViewController
import UIKit
class ImageDetailViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var productImage: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var productName: UILabel!
var img:UIImage!
var name:String!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
productName.text = name
productImage.image = img
}
}
DemoCollectionViewCell.swift
import UIKit
class DemoCollectionViewCell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var productImage: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var productName: UILabel!
}
Output

